昊为泰生物多年专注于深耕遗传学和基因组学等领域科研特色技术的开发,不断跟进国际先进的科研成果及技术发展,创新研发了许多特色专利技术和领域内前沿的检测服务项目,受到广大专业科研用户的认可和好评。
昊为泰生物自主研发的创新技术--Accu16S®细菌绝对定量测序,是通过向样品DNA中添加人工合成的不同拷贝数的spike-in 内标序列,之后进行16S rDNA扩增子文库构建、测序,再根据spike-in 内标的16S rDNA扩增子reads数及其绝对拷贝数绘制出标准曲线,后就成功获得样品中OTU代表序列对应的细菌物种绝对拷贝数。
简单的说,相对定量是由测序reads得到OTU,然后经过抽平后再进行生信分析。而绝对定量是在获得测序reads,得到OTU后,不抽平,而是直接利用标准曲线换算成绝对拷贝数后进行分析。
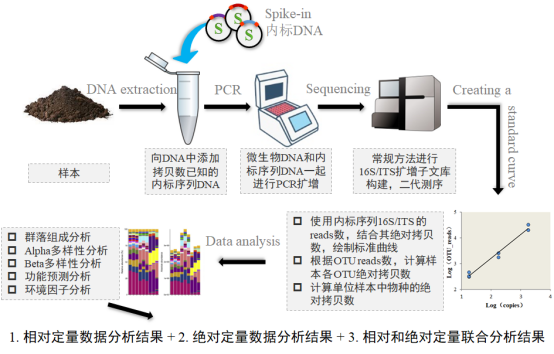
试验及分析流程
技术优势
• 一次检测,三套数据,结果更丰富;
• 对样本的需求量要求低,避免因样本无备份等造成的无法检测情况;
• 检测通量高,检测合格范围内各类菌种均可绝对定量;
• 相对定量和绝对定量数据相互印证,减少传统相对定量假阳性问题;
• 避免跨平台qPCR定量的系统误差;
• 避免因样本DNA抽提等原因造成的PCR抑制剂残留对结果准确性的影响;
• 避免qPCR等定量实验碰到的引物设计和优化难题。
样本类型:DNA、土壤、粪便或其他环境样本
DNA需求量:浓度 ≥ 20ng/μL,总量 ≥500 ng (一个片段,两次实验需求量)
样本完整度:琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测基因组DNA完整性,要求电泳条带清晰可见,无明显降解,且无RNA污染
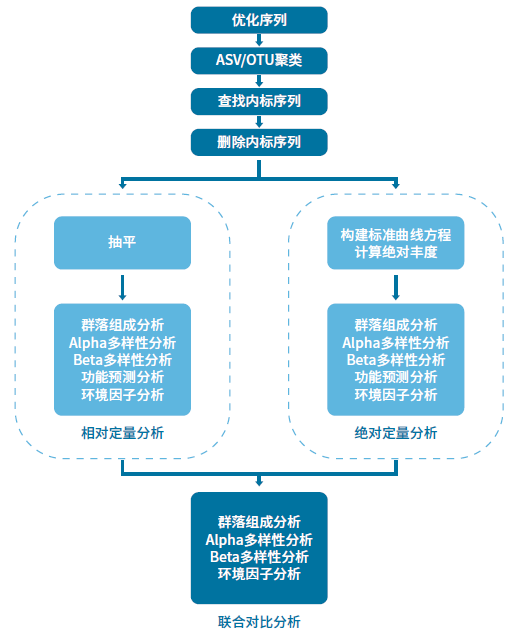
Accu16S®细菌绝对定量测序技术的数据分析包括:序列质量控制、序列比对和OTU聚类、物种注释、标准曲线构建、样本绝对丰度计算和分析等步骤。分析结果包括各菌群不同分类水平的绝对丰度、相对丰度和联合分析等内容。
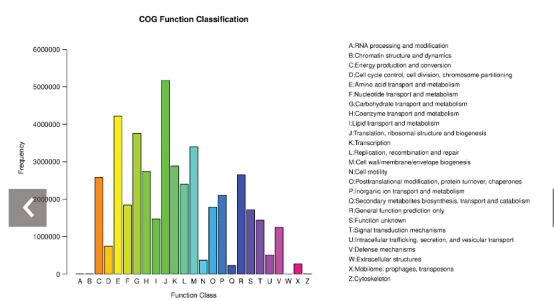
功能预测(PICRUSt2)
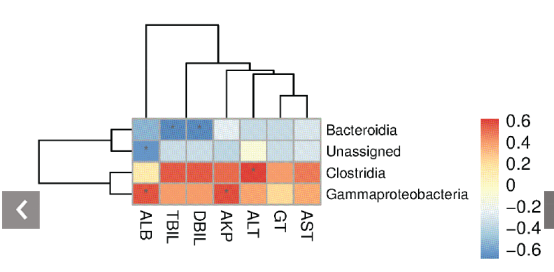
物种与环境因子相关性分析
— 医学领域(部分)—
文章 | 杂志 | IF | 年份 | 单位 | 样本类型 |
Glucocorticoid-induced loss of beneficial gut bacterial extracellular vesicles is associated with the pathogenesis of osteonecrosis 糖皮质激素诱导的肠道有益菌胞外囊泡的减少与骨坏死发病相关 | Science Advances | 14.957 (JCR: Q1) | 2022 | 中南大学湘雅医院 | 小鼠粪便 |
Chain conformation, physicochemical properties of fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from sea cucumber Stichopus chloronotus and its in vitro fermentation by human gut microbiota 绿刺参岩藻糖基硫酸软骨素的链构象、理化性质及其体外发酵 | Carbohydrate Polymers | 10.723 (JCR: Q1) | 2019 | 潍坊医学院 | 人类粪便 体外发酵液 |
Bacteriophages allow selective depletion of gut bacteria to produce a targeted-bacterium-depleted mouse model 噬菌体可以通过对肠道细菌的选择性敲除产生靶向敲除细菌小鼠模型 | Cell Reports Methods | Cell子刊,暂无 | 2022 | 西安交通大学第一附属医院 | 小鼠粪便 |
Network Pharmacology and Absolute Bacterial Quantification-Combined Approach to Explore the Mechanism of Tianqi Pingchan Granule Against 6-OHDA-Induced Parkinson’s Disease in Rats 利用网络药理学与细菌绝对定量相结合的方法探讨天芪平颤颗粒抗6-OHDA诱发大鼠帕金森病的作用机制 | Frontiers in Nutrition | 6.590 (JCR: Q1) | 2022 | 上海交通大学医学院附属新华医院 | 大鼠粪便 |
Effects of β-type glycosidic polysaccharide from Flammulina velutipes on anti-inflammation and gut microbiota modulation in colitis mice 金针菇β-型糖苷多糖对结肠炎小鼠的抗炎及肠道菌群调节作用 | Food & Function | 6.317 (JCR: Q1) | 2020 | 南京农业大学 | 小鼠粪便 |
Supplemental N acyl homoserine lactonase alleviates intestinal disruption and improves gut microbiota in broilers challenged by Salmonella Typhimurium 补充N-酰基高丝氨酸内酯酶可减轻受鼠伤寒沙门氏菌攻击的肉鸡的肠道紊乱并改善肠道菌群 | Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology | 6.175 (JCR: Q1) | 2023 | 华南农业大学 | 肉鸡肠道内容物 |
Accurate 16S Absolute Quantification Sequencing Revealed Vaginal Microecological Composition and Dynamics During Mixed Vaginitis Treatment With Fufang FuRong Effervescent Suppository 准确的16S绝对定量测序揭示复方芙蓉泡腾栓治疗混合性阴道炎的阴道微生态组成和动态 | Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology | 6.073 (JCR: Q1) | 2022 | 清华大学临床医学院 | 阴道拭子 |
High-throughput absolute quantification sequencing revealed osteoporosis-related gut microbiota alterations in Han Chinese elderly 高通量绝对定量测序揭示汉族老年人骨质疏松症相关肠道微生物的变化 | Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology | 6.073 (JCR: Q1) | 2022 | 华中科技大学同济医学院 | 人类粪便 |
Cross-comparison of microbiota in the oropharynx, hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma and their adjacent tissues through quantitative microbiome profiling 利用定量微生物图谱分析来比较口咽、下咽鳞状细胞癌及其邻近组织中的微生物 | Journal of Oral Microbiology | 5.833 (JCR: Q1) | 2022 | 上海复旦大学附属医院 | 癌组织样本 和口咽拭子 |
Commensal Relationship of Three Bifidobacterial Species Leads to Increase of Bifidobacterium in Vitro Fermentation of Sialylated Immunoglobulin G by Human Gut Microbiota 三种双歧杆菌的共生关系导致双歧杆菌在含有唾液酸化免疫球蛋白G的人类肠道菌群体外发酵中数量增加 | Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry | 5.895 (JCR: Q1) | 2020 | 南京农业大学 | 人类粪便 体外发酵液 |
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor protects mice against hepatocellular carcinoma by ameliorating intestinal dysbiosis and attenuating inflammation 粒细胞-巨噬细胞集落刺激因子可以通过改善肠道失调和减轻炎症来保护小鼠免受肝细胞癌侵害 | World Journal of Gastroenterology | 5.374 (JCR: Q2) | 2020 | 中国科学院西北生态环境资源研究院 | 小鼠粪便 |
The Genus Parabacteroides Is a Potential Contributor to the Beneficial Effects of Truncal Vagotomy-Related Bariatric Surgery 副杆菌属是躯干迷走神经切开术相关减肥手术有益效果的潜在贡献者 | Obesity Surgery | 3.479 (JCR: Q2) | 2022 | 海军医科大学 | 小鼠粪便 |
— 环境农学食品领域(部分)—
文章 | 杂志 | IF | 年份 | 单位 | 样本类型 |
A marine bacterial community capable of degrading poly(ethylene terephthalate) and polyethylene 一种能够降解聚乙烯对苯二甲酸酯和聚乙烯的海洋细菌群落 | Journal of Hazardous Materials | 14.224 (JCR: Q1) | 2021 | 中国科学院海洋研究所 | 塑料污染物 |
Transcriptomic evidences for microbial carbon and nitrogen cycles in the deoxygenated seawaters of Bohai Sea 渤海脱氧海水中微生物碳氮循环的转录组学证据 | Environment International | 13.352 (JCR: Q1) | 2022 | 厦门大学 | 水体生物膜 |
The synergy of porous substrates and functional genera for efficient nutrients removal at low temperature in a pilot-scale two-stage tidal flow constructed wetland 中试规模两级潮汐流人工湿地中多孔基质和功能菌属的协同作用对低温下营养物质的高效去除 | Bioresource Technology | 11.889 (JCR: Q1) | 2021 | 北京工业大学 | 水体生物膜 |
Quantitative ecology associations between heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification, nitrogen-metabolism genes, and key bacteria in a tidal flow constructed wetland 潮汐流人工湿地异养硝化-好氧反硝化、氮代谢基因和关键细菌之间的数量生态学关联 | Bioresource Technology | 11.889 (JCR: Q1) | 2021 | 北京工业大学 | 水体生物膜 |
Response of microbial communities based on full-scale classification and antibiotic resistance genes to azithromycin and copper combined pollution in activated sludge nitrification laboratory mesocosms at low temperature 低温下活性污泥硝化系统中基于全尺度分类的微生物群落和抗生素抗性基因对阿奇霉素和铜复合污染的响应 | Bioresource Technology | 11.889 (JCR: Q1) | 2021 | 北京工业大学 | 活性污泥 |
Sediments alleviate the inhibition effects of antibiotics on denitrification: Functional gene, microbial community, and antibiotic resistance gene analysis 沉积物减缓抗生素对反硝化作用的抑制作用:功能基因、微生物群落和抗生素抗性基因分析 | Science of The Total Environment | 10.753 (JCR: Q1) | 2022 | 北京大学 | 悬浮沉积物 |
Geographical, climatic, and soil factors control the altitudinal pattern of rhizosphere microbial diversity and its driving effect on root zone soil multifunctionality in mountain ecosystems 地理、气候和土壤因子调控山地生态系统根际微生物多样性的海拔格局及其对根区土壤多功能性的驱动作用 | Science of The Total Environment | 10.753 (JCR: Q1) | 2023 | 宁夏大学 | 土壤 |
High-throughput absolute quantification sequencing reveals the effect of different fertilizer applications on bacterial community in a tomato cultivated coastal saline soil 高通量微生物绝对定量测序揭示不同施肥应用对种植番茄的滨海盐渍土壤细菌群落的影响 | Science of The Total Environment | 10.753 (JCR: Q1) | 2019 | 南京农业大学 | 土壤 |
Long-term nitrogen application decreases the abundance and copy number of predatory myxobacteria and alters the myxobacterial community structure in the soil 长期施氮降低了捕食性粘细菌的相对丰度和绝对拷贝数,改变了土壤中粘细菌群落结构 | Science of The Total Environment | 10.753 (JCR: Q1) | 2019 | 中国科学院南京土壤所 | 土壤 |
Home-based microbial solution to boost crop growth in low-fertility soil 促进低肥力土壤作物生长主场优势的微生物解决方案 | New Phytologist | 10.32 (JCR: Q1) | 2023 | 中国科学院南京土壤所 | 土壤 |
Response of Rhizosphere Bacterial Communities to Near-Natural Forest Management and Tree Species within Chinese Fir Plantations 杉木人工林根际细菌群落对近自然森林经营及树种的响应 | Microbiology Spectrum | 9.043 (JCR: Q1) | 2023 | 中国林业科学研究院林业研究所 | 土壤 |
Storage tank as a pretreatment unit for rainwater cleaner production: Role of biofilm bacterial communities and functional genera in water quality improvement 作为雨水清洁生产预处理单元的蓄水池:生物膜细菌群落和功能菌属在水质改善中的作用 | Journal of Environmental Management | 8.910 (JCR: Q1) | 2022 | 北京工业大学 | 水体生物膜 |
Insights into the bacterial, fungal, and phage communities and volatile profiles in different types of Daqu 不同类型大曲中的细菌、真菌和噬菌体群落及挥发性物质研究 | Food Research International | 6.475 (JCR: Q1) | 2022 | 中国农业大学 | 酒类发酵物 |
Intercropping Pinto Peanut in Litchi Orchard Effectively Improved Soil Available Potassium Content, Optimized Soil Bacterial Community Structure, and Advanced Bacterial Community Diversity 荔枝园间作平托花生有效提高了土壤速效钾含量,优化了土壤细菌群落结构,提高了细菌群落多样性 | Frontiers in Microbiology | 6.064 (JCR: Q1) | 2022 | 海南省农业科学院 | 土壤 |
Response of soil bacterial community to agricultural reclamation in the Tengger desert, northwestern China 腾格里沙漠土壤细菌群落对农业开垦的响应 | Applied Soil Ecology | 5.509 (JCR: Q2) | 2022 | 宁夏大学 | 土壤 |
1、目前天昊微生物绝对定量测序是细菌和真菌都能检测吗?检测哪些区段?
答:是的。Accu16S®细菌绝对定量测序可以检测的区段包括16S rDNA的V3、V4、V3+V4和V4+V5区。AccuITSTM真菌绝对定量测序可以检测的区段为ITS1和ITS2区。其他功能基因和18S rDNA暂不提供检测服务。
2、天昊微生物绝对定量测序能得到目前市场上其他公司的常规扩增子测序结果吗?
答:可以的。目前其他公司常见的常规扩增子测序就是传统的相对定量测序。我们绝对定量一次检测,可以提供常规的相对定量结果、绝对定量结果,以及两者比对分析结果三部分,数据更加全面。
3、天昊微生物绝对定量测序能检测什么样本?
答:研究领域涉及医学、环境、农学和生态等各个领域,样本类型包括人类及动物粪便、土壤、体外发酵液、水体生物膜、酒类发酵物及口拭子DNA样本等。
4、我们应该如何取样?
答:取样需要重点注意四个方面,即一致性、低温、洁净和备份。因为样本类型多样,如果不熟悉如何操作,可以在取样前,联系天昊技术人员进行咨询。
5、如果送到样本是DNA,应该注意哪些问题?
答:天昊绝对定量测序可以根据客户要求,选择用基于DNA水平或者样本水平进行分析(DNA水平:copies/ ng DNA;样本水平:copies/g土壤、粪便、copies/ L 水样等)。因此,如果客户寄送样本为DNA,而后希望按照样本水平进行分析,则客户在自己抽提DNA之前,需要对提取样本的重量或者液体体积进行记录。
6、天昊绝对定量测序有生信分析的专属云平台吗?
答:有的。客户可以登陆我们的云平台进行数据的二次自主分析。




copyright © 2008-2023 昊为泰 reserved. ICP备案序号: